Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yoshida, Kenta*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Inoue, Koji*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*; Shimodaira, Masaki
Materia, 62(3), p.154 - 158, 2023/03
no abstracts in English
Takamizawa, Hisashi; Hata, Kuniki; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Toyama, Takeshi*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 556, p.153203_1 - 153203_10, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:31.78(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Solute clusters (SCs) formed in pressurized water reactor surveillance test specimens neutron-irradiated to a fluence of 1  10
10 n/cm
n/cm were analyzed via atom probe tomography to understand the effect of silicon on solute clustering and irradiation embrittlement of reactor pressure vessel steels. In high-Cu bearing materials, Cu atoms were aggregated at the center of cluster surrounded by the Ni, Mn, and Si atoms like a core-shell structure. In low-Cu bearing materials, Ni, Mn, and Si atoms formed cluster and these solutes were not comprised core-shell structure in SCs. While the number of Cu atoms in clusters was decreased with decreasing nominal Cu content, the number of Si atoms had clearly increased. The cluster radius (
were analyzed via atom probe tomography to understand the effect of silicon on solute clustering and irradiation embrittlement of reactor pressure vessel steels. In high-Cu bearing materials, Cu atoms were aggregated at the center of cluster surrounded by the Ni, Mn, and Si atoms like a core-shell structure. In low-Cu bearing materials, Ni, Mn, and Si atoms formed cluster and these solutes were not comprised core-shell structure in SCs. While the number of Cu atoms in clusters was decreased with decreasing nominal Cu content, the number of Si atoms had clearly increased. The cluster radius ( ) and number density (
) and number density (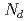 ) decreased and increased, respectively, with increasing nominal Si content. The shift in the reference temperature for nil-ductility transition (
) decreased and increased, respectively, with increasing nominal Si content. The shift in the reference temperature for nil-ductility transition ( RT
RT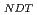 ) showed a good correlation with the square root of volume fraction (
) showed a good correlation with the square root of volume fraction (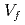 ) multiplied by r (
) multiplied by r (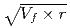 ). This suggested that the dislocation cutting through the particles mechanism dominates the precipitation hardening responsible for irradiation embrittlement. The negative relation between the nominal Si content and
). This suggested that the dislocation cutting through the particles mechanism dominates the precipitation hardening responsible for irradiation embrittlement. The negative relation between the nominal Si content and  RT
RT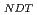 indicated that increasing of nominal Si content reduces the degree of embrittlement.
indicated that increasing of nominal Si content reduces the degree of embrittlement.
Takamizawa, Hisashi; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 143(5), p.051502_1 - 051502_8, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:30.36(Engineering, Mechanical)no abstracts in English
Hata, Kuniki; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Hojo, Tomohiro*; Ebihara, Kenichi; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 543, p.152564_1 - 152564_10, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:91.16(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Reactor pressure vessel (RPV) steels for pressurized water reactors (PWRs) with bulk P contents ranging from 0.007 to 0.012wt.% were subjected to neutron irradiation at fluences ranging from 0.3 to 1.2 10
10 n/cm
n/cm (E
(E  1 MeV) in PWRs or a materials testing reactor (MTR). Grain-boundary P segregation was analyzed using Auger electron spectroscopy (AES) on intergranular facets and found to increase with increasing neutron fluence. A rate theory model was also used to simulate the increase in grain-boundary P segregation for RPV steels with a bulk P content up to 0.020wt.%. The increase in grain-boundary P segregation in RPV steel with a bulk P content of 0.015wt.% (the maximum P concentration found in RPV steels used in Japanese nuclear power plants intended for restart) was estimated to be less than 0.1 in monolayer coverage at 1.0
1 MeV) in PWRs or a materials testing reactor (MTR). Grain-boundary P segregation was analyzed using Auger electron spectroscopy (AES) on intergranular facets and found to increase with increasing neutron fluence. A rate theory model was also used to simulate the increase in grain-boundary P segregation for RPV steels with a bulk P content up to 0.020wt.%. The increase in grain-boundary P segregation in RPV steel with a bulk P content of 0.015wt.% (the maximum P concentration found in RPV steels used in Japanese nuclear power plants intended for restart) was estimated to be less than 0.1 in monolayer coverage at 1.0 10
10 n/cm
n/cm (E
(E  1 MeV). A comparison of the PWR data with the MTR data showed that neutron flux had no effect upon grain-boundary P segregation. The effects of grain-boundary P segregation upon changes in irradiation hardening and ductile-brittle transition temperature (DBTT) shifts were also discussed. A linear relationship between irradiation hardening and the DBTT shift with a slope of 0.63 obtained for RPV steels with a bulk P content up to 0.026wt.%, which is higher than that of most U.S. A533B steels. It is concluded that the intergranular embrittlement is unlikely to occur for RPV steels irradiated in PWRs.
1 MeV). A comparison of the PWR data with the MTR data showed that neutron flux had no effect upon grain-boundary P segregation. The effects of grain-boundary P segregation upon changes in irradiation hardening and ductile-brittle transition temperature (DBTT) shifts were also discussed. A linear relationship between irradiation hardening and the DBTT shift with a slope of 0.63 obtained for RPV steels with a bulk P content up to 0.026wt.%, which is higher than that of most U.S. A533B steels. It is concluded that the intergranular embrittlement is unlikely to occur for RPV steels irradiated in PWRs.
Takamizawa, Hisashi; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Hirano, Takashi*
Proceedings of ASME 2020 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2020) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2020/08
no abstracts in English
Takamizawa, Hisashi; Katsuyama, Jinya; Ha, Yoosung; Tobita, Toru; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Onizawa, Kunio
Proceedings of 2019 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2019) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2019/07
no abstracts in English
Takamizawa, Hisashi; Ito, Hiroto; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 479, p.533 - 541, 2016/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:49.29(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To understand neutron irradiation embrittlement in high fluence regions, statistical analysis using the Bayesian nonparametric (BNP) method was performed for the Japanese surveillance and material test reactor irradiation database. The BNP method is essentially expressed as an infinite summation of normal distributions, with input data being subdivided into clusters with identical statistical parameters (such as mean and standard deviation) for each cluster to estimate shifts in ductile-to-brittle transition temperature (DBTT). Clusters typically depend on chemical compositions, irradiation conditions, and the irradiation embrittlement. Specific variables contributing to the irradiation embrittlement include the content of Cu, Ni, P, Si, and Mn in the pressure vessel, neutron flux, neutron fluence, and irradiation temperatures. It was found through numerous examinations that the measured shifts of DBTT correlated well with calculated ones. Data associated with the same materials were subdivided into the same clusters even if neutron fluences were significantly disparate among the results. This indicates that slowly developing or late-onset embrittlement mechanisms were not evident in the present study.
Takamizawa, Hisashi; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Proceedings of 2016 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2016) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2016/07
It has been accepted that neutron irradiation embrittlement of reactor pressure vessel is caused by irradiation-induced formation of solute clusters (SCs) and matrix damages (MDs). In the present study, to analyze the contribution of chemical composition contained in SCs to irradiation embrittlement at high fluence region, statistical analysis using the Bayesian nonparametric (BNP) method was performed for Japanese PWR surveillance data. The significance of P, Si and Mn contents, which are not necessarily included in embrittlement correlations unlike the Cu and Ni content, was evaluated. The BNP method can learn the complexity of the statistical model itself from the input data and infer the predicted data with individual probability distribution of predict condition. The result suggested that irradiation embrittlement was most affected by the Si content at high fluence region.
Suzuki, Masahide; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Kinzoku, 71(8), p.42 - 45, 2001/08
no abstracts in English
Ishii, Toshimitsu; Ooka, Norikazu; Niimi, Motoji; Kobayashi, Hideo*
Kinzoku, 71(8), p.20 - 24, 2001/08
no abstracts in English
Tsukada, Takashi; Ebine, Noriya
Nihon AEM Gakkai-Shi, 9(2), p.171 - 177, 2001/06
no abstracts in English
Ebine, Noriya; Suzuki, Masahide
Nihon Oyo Jiki Gakkai-Shi, 25(4-2), p.1051 - 1054, 2001/04
no abstracts in English
Ishii, Toshimitsu; Ooka, Norikazu; Hoshiya, Taiji; Kobayashi, Hideo*
KURRI-KR-62, p.29 - 41, 2001/03
no abstracts in English
; Ooka, Norikazu; ; Saito, Junichi; Hoshiya, Taiji; *; Kobayashi, Hideo*
JAERI-Conf 99-009, p.163 - 172, 1999/09
no abstracts in English
; Ooka, Norikazu; Kobayashi, Hideo*
Proc. of 2nd Japan-US Symp. on Advances in NDT, p.151 - 156, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
Nishiyama, Yutaka; Fukaya, Kiyoshi; Onizawa, Kunio; Suzuki, Masahide; *; *; *; *
JAERI-Tech 98-041, 30 Pages, 1998/10
no abstracts in English
Onizawa, Kunio; Tobita, Toru; Suzuki, Masahide
JAERI-Research 97-081, 36 Pages, 1997/11
no abstracts in English
; Fukaya, Kiyoshi; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Suzuki, Masahide; Eto, Motokuni; Omi, Masao; Mimura, Hideaki; Ooka, Norikazu
JAERI-Research 96-028, 33 Pages, 1996/06
no abstracts in English
Onizawa, Kunio; Suzuki, Masahide
IWG-LMNPP-95/5 (Vol. I), 0, p.279 - 293, 1995/00
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Masahide; Onizawa, Kunio; Kizaki, Minoru
JAERI-Research 94-015, 74 Pages, 1994/09
no abstracts in English